Tympanoplasty
Tympanoplasty is a surgical procedure performed by ENT specialists to repair and reconstruct the eardrum
(tympanic membrane) and the small bones in the middle ear. This procedure is crucial for individuals with perforated eardrums, chronic ear infections, or hearing loss related to middle ear issues. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore tympanoplasty in detail, covering everything from its indications to postoperative care.
1. What is the condition about?
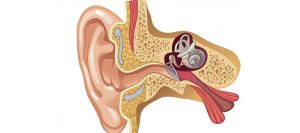
The tympanic membrane, or eardrum, is a delicate, thin membrane that separates the external ear canal from the middle ear. It plays a vital role in transmitting sound vibrations to the middle ear. When the eardrum is damaged due to infection, trauma, or other factors, it can result in hearing loss, recurrent ear infections, and other complications. Tympanoplasty aims to restore the integrity of the eardrum, improving hearing and preventing further infections.

2. What are the causes?

- Chronic Ear Infections : Repeated or untreated ear infections can weaken the eardrum over time.
- Trauma : Injury to the ear, such as a direct blow or insertion of foreign objects, can cause eardrum damage.
- Barotrauma : Sudden changes in air pressure, often experienced during air travel or scuba diving, can lead to eardrum perforation.
- Middle Ear Surgery : Complications from previous ear surgeries may result in eardrum issues.
3. How common is the condition?
Tympanic membrane perforations are relatively common and can affect individuals of all ages. They are often associated with chronic ear infections, particularly in children. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment can prevent
complications and the need for surgery.
4. What can an ENT Specialist do for you?
An ENT specialist plays a crucial role in the evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment of eardrum issues. Initially, they will perform a thorough examination of the ear, including audiometric tests to assess hearing loss. If non-surgical treatments, such as antibiotics or ear drops, do not resolve the problem, tympanoplasty may be recommended.
5. How can the condition be treated?
Tympanoplasty is the primary treatment for eardrum perforations and related middle ear issues. The procedure involves the following steps:

Anesthesia
Tympanoplasty is typically performed under general anesthesia to ensure patient comfort and safety.
Access
The surgeon makes a small incision either behind the ear or inside the ear canal to access the middle ear.
Tissue Graft

Reconstruction
If necessary, the surgeon may repair or reconstruct the small bones in the middle ear (ossicles) to improve hearing.

Closure
The incision is closed with sutures or other closure methods.
6. Guidelines for Surgery
Tympanoplasty is a well-established surgical procedure with established guidelines :
- Patients should follow preoperative instructions, which may include fasting before surgery and discontinuing certain medications.
- After surgery, keep the ear dry and avoid activities that could expose the ear to infection or trauma.
- Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments to monitor healing and hearing improvement.
7. Evaluation & Follow Up for Treatment
Postoperative care is crucial for a successful outcome. Patients will have several follow-up appointments to monitor healing, remove any packing or sutures, and assess hearing improvement. Audiometric tests will be conducted to measure hearing progress.
8. Risks of Surgery
Like any surgical procedure, tympanoplasty carries certain risks, including infection, bleeding, hearing
deterioration, or graft failure. However, complications are relatively rare when the procedure is performed by an
experienced surgeon
9. Alternatives to Surgery
In some cases, non-surgical treatments, such as antibiotics or ear drops, may be effective in healing small eardrum perforations. However, if these methods do not yield positive results, tympanoplasty remains the most reliable and definitive treatment option.
In conclusion, tympanoplasty is a valuable surgical procedure that can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with eardrum issues and related hearing problems. If you suspect you may have a perforated eardrum or chronic ear infections, consult with an ENT specialist for a comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment plan, which may include tympanoplasty if deemed necessary.